HOME > Short-Term benefits > Illnesses and Injuries
|
Members and their dependents (excluding those under the late-stage geriatric medical plan) who become ill or injured for reasons not related to official duties can receive necessary treatment at hospitals that provide insurance-covered medical services by presenting their My Number Card registered for use as a Health Insurance Certificate. [You must complete advance procedures before you can use your My Number Card as your Health Insurance Certificate.] 1. Using a My Number Card as a Health Insurance Certificate | Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare website |
| Treatments for illnesses and injuries related to official duties are eligible for compensation under as stipulated in the Government Employees' Accident Compensation Act and other government-related laws, and the Mutual Aid Association does not pay the benefits. |
1Medical Treatment Benefit and Family Medical Treatment Benefit
|
||||||||||||||||
| ∗1 | For members who (1) are 70 years of age or older, (2) have the standard monthly salary of 280,000 yen or more, and (3) have a dependent or dependents who are early-stage senior recipients, the specified amount is 5,200,000 yen or more, including the income of the dependent or dependents (3,830,000 yen or more if all members are early-stage senior recipients). |
|
| ∗2 | Individuals who were born between April 2, 1939 and April 1, 1944 are eligible for special treatment for reduced responsibility. |
2Inpatient Dietetic Treatment Benefit and Inpatient Resident Treatment Benefit
|
||||
| 1. | Members pay a flat amount for meals while they or their dependents are hospitalized. The Mutual Aid Association will pick up the rest of the costs. | |||
| ii. | The meal copayment amounts per meal per person are as follows (the standard copayment). | |||
|
| Notes: | The patient’s responsibility (the standard responsibility amount) is not eligible for high-cost medical treatment costs, reimbursement of the partial cost benefits, or supplementary benefits for family medical treatment benefit. *1 through *3 apply to the member and his/her dependents only when the member himself/herself falls under the low-income earner category. |
|||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Elderly recipients hospitalized in a long-term care facility*1 pay a flat amount for meals and living expenses. The Mutual Aid Association will pick up the rest of the costs as inpatient resident treatment costs. The standard copayment amounts for inpatient resident treatment costs are as follows. | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| ∗1 | Ask your healthcare institution if the facility qualifies as a long-term care facility. | |||||||||||
| ∗2 | The amounts differ depending on healthcare institutions. Ask your healthcare institution which amount applies to you. | |||||||||||
| (1) | Patients who require a respirator, central venous feeding, or patients who have spinal injuries (with quadriplegia) or intractable diseases pay only the amounts equivalent to the cooking ingredients (the standard inpatient dietetic copayment). | |||||||||||
| (2) | Standard copayments are not eligible for high-cost medical treatment benefits, partial reimbursement of the cost of benefits, or supplementary benefits for family medical treatment costs. | |||||||||||
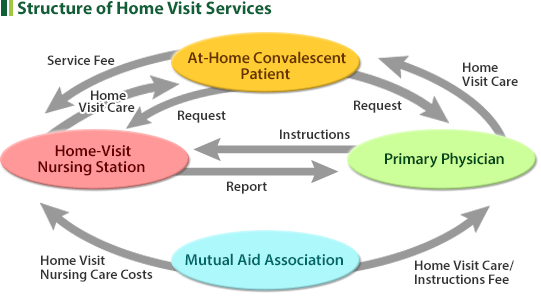
3Home Visit Nursing Care Benefit and Family Home Visit Nursing Care Benefit
| Members or their dependents who continue to receive treatment at home (i.e., the primary physician confirms that the home care requirements comply with the criteria stipulated by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare) can receive home visit care services of the nurses dispatched from qualified home visit nursing care organizations. |
| Notes: | The criteria stipulated by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare include patients with intractable diseases, terminal cancer patients, severely disabled patients (e.g., muscular dystrophy and brain paralysis), and middle-aged cerebral stroke patients. |
|
||
| The member who receives home visit care pays 30% of the costs, with the remainder paid by the Mutual Aid Association. |
|
||
| The dependent who receives home visit care pays 30% of the costs, with the remainder paid by the Mutual Aid Association. |
 |
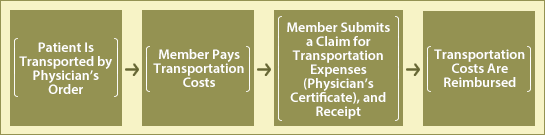
4Transportation Benefit and Family Transportation Benefit
| When the member or his/her dependent who is non-ambulatory due to the severity of his/her illness is incapable of using public transit and is transported via a bed-equipped car or taxi by the physician’s order, the Mutual Aid Association will, at a later date, pay the transportation costs that the Association approves if it receives a request from the member. |
| i. | If the accompaniment of a caretaker (other than relatives such as parents and siblings) is needed, the transportation costs for that caretaker will also be paid. | |
| ii. | Transportation costs for regular hospital visits are not paid. |
 |
5Partial Reimbursement of the Cost of Benefits and Supplementary Benefit for Family Medical Treatment Costs
| If the member’s or his/her dependent’s copayment amount to the same hospital or pharmacy exceeds 25,000 yen (50,000 yen for combined household high-cost medical treatment benefits) per event per person per month, the Mutual Aid Association will, at a later date, pay the excess amount as partial reimbursement of the cost of benefits to the member, and as supplementary benefit for family medical treatment costs to the dependent. However, the Association will not pay any excess amount less than 1,000 yen, and the payment amounts will be rounded down to the nearest 100 yen. |
| ∗ | Members whose standard monthly salary is 530,000 yen and more (high-income earners) and their dependents have new responsibility amounts starting with medical treatments in October 2013, as follows: |
|||||||||||||
| High-Income Earners' Maximum Responsibilities for Supplementary Benefits | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
The provision applies to the supplementary benefit for family home visit nursing care costs. |
| 1. | The amount of copayment does not include the standard copayment due for hospitalization. If high-cost medical treatment benefits are paid for, the Association will pay the amount after deducting the reimbursement amount for high-cost medical treatment. | |
| 2. | These benefits will not be available when the municipal government subsidizes the member’s partial copayment to healthcare organizations. In this case, the member should inform the Association. | |
| 3. | The Association calculates supplementary benefits and other benefits based on the itemized statement of medical treatment fees. For this reason, the Association’s benefit amounts may be slightly different from those calculated based on the amounts paid at the cashiers of healthcare organizations. |
6High-Cost Medical Treatment Benefit
| If the copayment amount that the member or his/her dependents pays for services by the same healthcare organization in the same month exceeds a specified amount (the copayment cap), the Mutual Aid Association will pay the patient, as a high-cost medical treatment benefit, any amount exceeding the copayment cap. |
| 1. | High-cost medical treatment benefits are calculated based on each monthly invoice (itemized statement of medical treatment fees) per patient created by the healthcare organization. Thus, these costs are calculated separately for medical and dental, and also separately for inpatient and outpatient services. | |
| 2. | The amount of copayment does not include the standard copayment due for hospitalization. |
| (1) | When a patient younger than 70 years old pays a copayment exceeding the upper limit in any given month for an insured medical treatment, the Association will pay the amount exceeding the amount calculated based on Table 1 (the copayment cap). Elderly recipients receive the amount exceeding the amount calculated based on Table 2 (the copayment cap). |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (2) | When a patient younger than 70 years old has received two or more invoices, each with the monthly copayment amount of 21,000 yen or more per event: When the same household has two or more invoices, each with the copayment amount of 21,000 yen (10,500 yen for the month in which the insurance plan switches to the late-stage geriatric medical care plan) or more per event in a single month, the Association will pay the amount exceeding the amount calculated based on Table 1 if the total of the copayment amounts of family members (called the combined household amount) exceeds 81,000 yen (150,000 yen for high-income earners). Elderly recipients receive the amount calculated based on Table 2. For the combined household of elderly recipients and recipients younger than 70 years old, the amount exceeding the calculated amount based on Table 3 will be paid. All amounts of copayments borne by elderly recipients can be included in the combined household amounts. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (3) | When the same household has multiple high-cost medical treatment benefits: When the same household has received high-cost medical treatment benefits for three months or longer (multiple medical expense statements) during the one-year period prior to the month in which a patient or patients receive treatment, the benefit amount for the fourth month and beyond is subject to reduction.(For details, see Table (1), Table (2) and (3).) However, the number of coverage provided solely under the outpatient copayment cap rule applicable to publicly subsidized medical treatments, specific diseases, and elderly recipients are excluded from the count. |
|
| Note: For the month in which the insurance plan switches to the late-stage geriatric medical care plan, the patient’s copayment cap is 1/2 of the applicable copayment cap. | ||
| (4) | Special cases for patients who require high costs medical care for a prolonged period If the patient has hemophilia or is under dialysis treatment for chronic renal failure, and his/her copayment amount exceeds 10,000 yen (20,000 yen for high-income earners and any dependents 70 years old or younger on dialysis who are supported by a member (regardless of his/her age) who earns a standard monthly salary of 530,000 yen or more, and 1/2 of each applicable cap for the month in which the insurance plan switches to the late-stage geriatric medical care plan), the Association pays the excess amount as a high-cost medical treatment benefit. |
| To be qualified for these special cases, submit an Application for Specific Disease Treatment Qualification to the Association. If you do not have a My Number Card registered for use as your Health Insurance Certificate, have a Certificate of Specific Disease Treatment Qualification issued. |
Certificate of Application of Copayment Cap For high-cost medical treatment benefits, the member or his/her dependent usually pays the entire amount of his/her copayment to the cashier of the healthcare organization at the time the patient uses the services of that organization for the illness or injury covered by the insurance. The Association will pay the patient the amount exceeding the patient’s copayment portion after a specified length of time. With the patient temporarily paying the entire amount of his/her copayment, the financial burden is not small. |
7High-Cost Nursing Care Combined Household Treatment Benefit
| If there is a member of the household who is receiving the benefit of a nursing care insurance, and if the combined household costs of the patients’ annual (from August 1 to July 31 of the following year) responsibility amounts for the medical insurance and the home nursing care insurance become significantly high, the Mutual Aid Association will pay the amount exceeding the patients’ maximum responsibility amounts according to the ratio of the patients’ responsibility amounts for the medical and home nursing care insurances, in order to ease the financial burden. |
| Note: | The home nursing care insurance pays the benefit as a “high-cost medical treatment benefit combined household nursing care service fee.” |
8Payments of Differences by Patients for Medical Treatment Costs and Medical Treatment Costs Combined With Non-Insured Costs
| Payments of differences by patients for medical treatment costs include the following. The benefit payments are the same as for regular insurance-covered treatments. However, the differences are not part of the benefits. |
| (1) | Hospital Room Upgrade If the patient upgrades his/her hospital room to one with a better condition (individual room or room for two patients), he/she is responsible for the difference in the cost. |
|
| (2) | Dental Treatments Certain limits are in place for each material used in dental treatments. If the patient wishes to use materials such as gold alloy and platinum, he/she is billed for the excess cost of materials incurred beyond the scope of the coverage, subject to the treatment method. |
|
| (3) | Advanced Technology Treatments When the patient receives advanced technology treatment, the insurance will cover the basic treatment (e.g., initial consultation and lab tests) part of that treatment as medical treatment cost combined with uninsured care costs. |
|
| As a general rule, you must present your My Number Card as your Health Insurance Certificate or similar document to a healthcare institution to receive treatment for illness or injury. If you cannot use your My Number Card as your Health Insurance Certificate due to an emergency or other unavoidable circumstances, including those given below, you must pay the full medical care cost up front. If the Association recognizes the circumstances, it will reimburse later as medical treatment benefits. |
| (1) | When the patient receives medical treatment in an area where no insured medical care facility is available | |
| (2) | When the patient receives medical treatment in the nearest medical care facility providing uninsured care due to an accident or sudden illness | |
| (3) | When the patient has purchased blood for transfusion, or therapeutic apparatus such as a prosthetic arm or leg, and corset. | |
| (4) | When the patient receives medical treatment overseas |
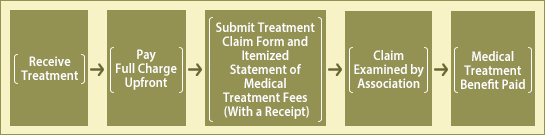
1Upfront Payment of Full Charge for Medical Treatment Costs
| The Association pays back to the patient the amount after deducting the patient’s responsibility from an amount obtained from a specified criterion as a medical treatment cost (medical treatment cost for a dependent or family). |
| 1. | Medical costs are higher when you pay the full charge upfront than when you use your insurance. Because the benefit amount that the Mutual Aid Association pays is calculated using insurance points, it may be lower than the actual amount you paid upfront. | |
| 2. | To claim your benefit, a receipt for medical treatment charges and an itemized statement are required. Please do not forget to obtain these from the healthcare organization |
 |
2Temporary Upfront Payment of Full Charge for Acupuncture, Moxacautery, and Massage
| When the patient suffers a fractured bone, bone dislocation, or sprain that requires treatment and receives treatment from an acupuncture, moxacautery, or massage therapist upon approval of a physician, the Mutual Aid Association will, at a later date, pay the treatment cost(s) that it approves based on a specific criterion. |
 |
3Temporary Upfront Payment of Full Charge for Therapeutic Apparatus
| When the patient purchases therapeutic apparatus such as prosthetic joints, a corset, or other therapeutic apparatus that the physician approves as necessary, the Mutual Aid Association will, at a later date, pay the cost of that apparatus based on a specific criterion. |
| The Association pays for therapeutic apparatus necessary for treatment purposes only. It will not pay for devices that remedy inconveniences in daily life or at work, or for those worn for cosmetic reasons (e.g., eyeglasses and hearing aids). |
 |
4Temporary Upfront Payment of Full Charge for Transfusion
| When the patient pays for blood for transfusion, the Mutual Aid Association will pay that cost as a treatment benefit at a later date. |
| The Association will not pay for the blood provided by a relative. |
 |
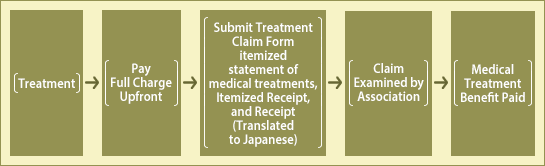
5Temporary Upfront Payment of Full Charge for Treatments Received Overseas
| If the patient receives and pays for treatment at an overseas healthcare organization for illness or injury, the Mutual Aid Association will pay the medical treatment benefit at la later date. The Association will not pay the benefit for the medical treatment that the patient received and paid for overseas when the patient travels there for the purpose of treatment. |
| 1. | Because the benefit amount that the Mutual Aid Association pays is calculated based on a Japanese domestic criterion (using insurance points), the benefit is almost always lower than the actual amount you paid out of pocket due to differences in healthcare practices between Japan and overseas. | |
| 2. | To claim your benefit, an itemized statement of medical treatments and an itemized receipt, and a receipt (issued locally) are required. Please do not forget to obtain these from the healthcare organization. | |
| 3. | You may submit an itemized statement of medical treatments and an itemized receipt Issued by the local healthcare organization. However, we recommend that you obtain specific forms before you travel. If you will be overseas for a long time, please inquire at the mutual aid department of your local branch in advance. | |
| 4. | When traveling overseas, we recommend that you purchase, for reassurance, an overseas travelers' personal accident insurance, which compensates for costs incurred due to an unexpected accident, as well as illness and injury. |
 |
|
| Association members and their dependents can receive treatment for illness and injury by presenting their My Number Card registered for use as a Health Insurance Certificate or similar document at hospitals. However, please note that you cannot receive the following types of treatment using your My Number Card as your Health Insurance Certificate or similar document: |
|
|
| Physical examinations, immunization shots for influenza, dysentery, and other diseases, and vitamin shots as a procedure for relief of fatigue | |
|
|
| Cosmetic surgery (e.g., rhinoplasty, double-fold eyelids), procedures for gray hair, hirsutism, and atrichia, and removal of age spots and moles | |
|
|
| Artificial abortion for economical reasons | |
|
|
| The benefit for child delivery (or family child delivery) is paid for pregnancy of four months (85 days) or longer whether or not the pregnancy ends in normal birth, stillborn, miscarriage, premature birth, or artificial abortion. However, the benefit will not be paid for expenses related to the treatment provided by a physician in the course of normal delivery. |

